Assume creative expression is a system, and let’s try to reduce it to its basic elements. We build this model of creativity not because it’s right, but because it might help us see how much of our ideas about arts and creativity make sense only in a non-digital society, and how a digital society might turn those ideas on their head. All models are wrong; some are useful.
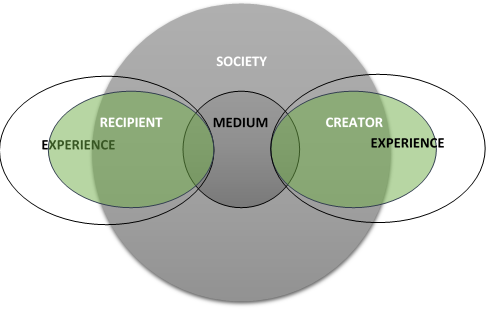
Anyone who performs a creative or interpretive act exists mostly in a social setting – mostly, because it is generally accepted that we all have access to some interior personal space that is both unique to us and not directly accessible to others. Together (the exterior and interior spaces in which we live) a person sees, hears, and feels the world around them and reacts in some way and for some purpose – that reaction is manifested in the working in some medium, some object we can transform to embody what we want to express. The result of that working then exists outside the person or persons that created it. The intent of that work is then received by someone who didn’t participate in its creation, but the work has meaning to the extent that the recipient reacts to it, drawing on their own external/internal experiences.
And of course the creator and the receiver are human beings. And of course the medium has no consciousness or will of its own, and is inert until the creator acts on it and invests his/her vision in it.
Just about every part of that attempt to abstract the creative process could be challenged, but this is a model not scripture so let’s play the game.
Take the world as we’ve known it, with its creators, its painters, sculptors, writers, playwrights and poets, and on the other side its audiences, its readers, viewers, theatre-goers, and in the middle the work, both the embodiment and the vehicle of what the creator has to say.
Can you think of any part of this world that isn’t being radcially transformed by the digital society?
Start with the creators: where is that line between the internal and external, when so much of what was private is now public, when what we see and hear in the world around us is filtered through algotrithms that are supposedly determined by our own behaviour and preferences?
Take receivers: well, there might not be any in a digital society. We are all “content creators” at some level. All we have to do is accept the terms and conditions of some cool thing that makes our lives easier, more fun, or that just makes us look good. We are being exhorted to control our own brand – our own interior lives are commodities too.
Finally, the medium: Steve Woodall, a book artist (and Collections Specialist for the Achenbach Foundation for Graphic Arts San Francisco) who used the relatively new technology of Xerox photocopiers, once said anything that shortens the distance between the artist and the audience is a good thing. The digital society creates the illusion that this distance has been illiminated – a potentially dangerous illusion since traditionally if you couldn’t acquire the raw materials of your medium yourself you could purchase them and in either case once acquired you were in control. In the digital society, you acquire the materials for free (subject to terms and conditions) and once acquired the product controls you. You rent, you pay for use, and you sell your interaction with the material back to the owner. But also this medium is not inert, the way a page that you write on is, or clay that you mould. It is intelligent. It shapes you as much as you shape it.
And of course all of them or none of them may be human beings. And these changes are not confined to artists and audiences. They are happening to all of us. The author and philosopher Bill Neblett wrote in Sherlock’s Logic that you can’t say you know what you mean to say if you can’t in fact say it – that thought outside expression can’t be known. Or as Wittgenstein said “whereof one cannot speak, one must remain silent.” Whatever we may think in our heads, it can’t be understood until it gets out of our heads and onto the page, the stage, the codebase, or wherever. In a traditional society, the inarticulate private space is fairly large and largely sacred – it is the source of personal value and dignity and is accepted at least in part as being outside of the public world we try to share with each other. In a digital society that private space is small because so much of it is now public, and what’s left behind is denigrated. How many of you have been asked to prove your friendship to someone by sharing one of their posts? And without a private personal unrecorded experience where is the room for history – the telling and retelling of stories, and the truth about human experience that stories can reveal – when experience is equated with the sum total of ones public interactions?
